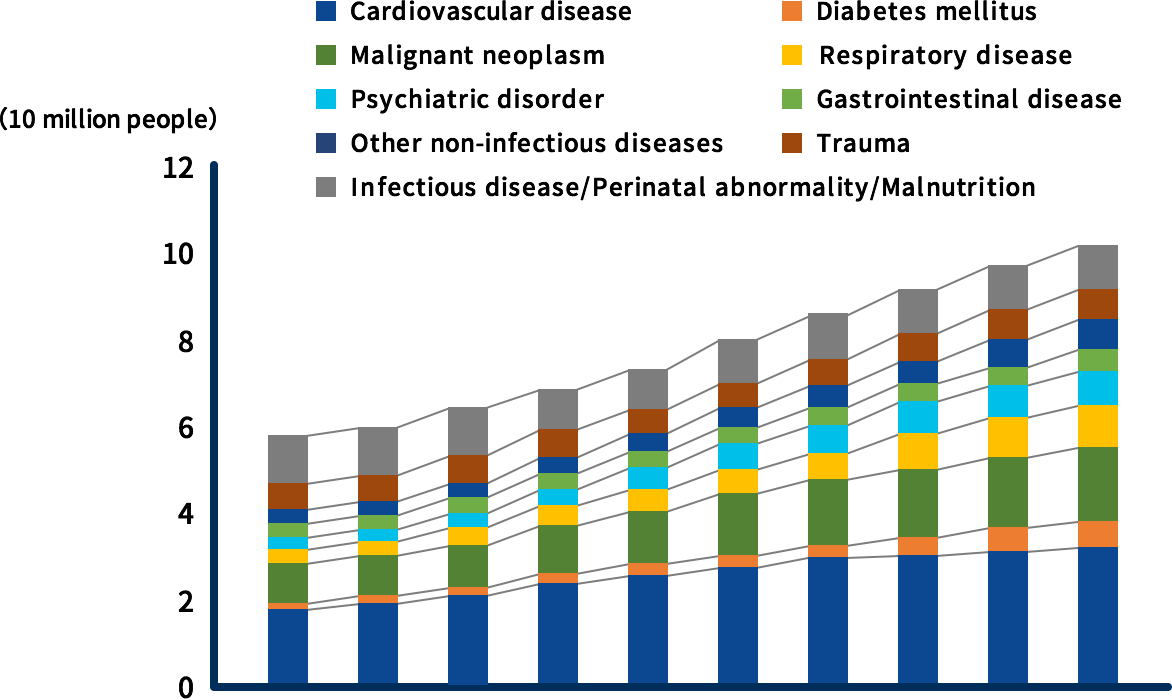
Market trend of lifestyle-related diseases
The number of patients with lifestyle-related diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases is expected to continue to increase with global population growth and lifestyle changes, accounting for around 30% to 40% of deaths worldwide.
Global cause of death
The pharmaceutical industry has recently tended to shift the emphasis from the area of lifestyle-related disease to other diseases due to the high cost of conducting large-scale clinical studies and maintaining global sales network; however, global mega-pharma and specialty pharma companies continue to invest in the area.
In addition, major pharma companies have attempted to accelerate the development by introducing late-stage assets from venture firms or acquiring companies, thereby accelerating specialized drug development in the industry.
In fact, 60% to 70% of drugs currently approved by the *FDA have been created by small and medium-sized companies such as drug discovery ventures.
*FDA: US Food and Drug Administration
Number of new drugs approved by FDA(By company size)
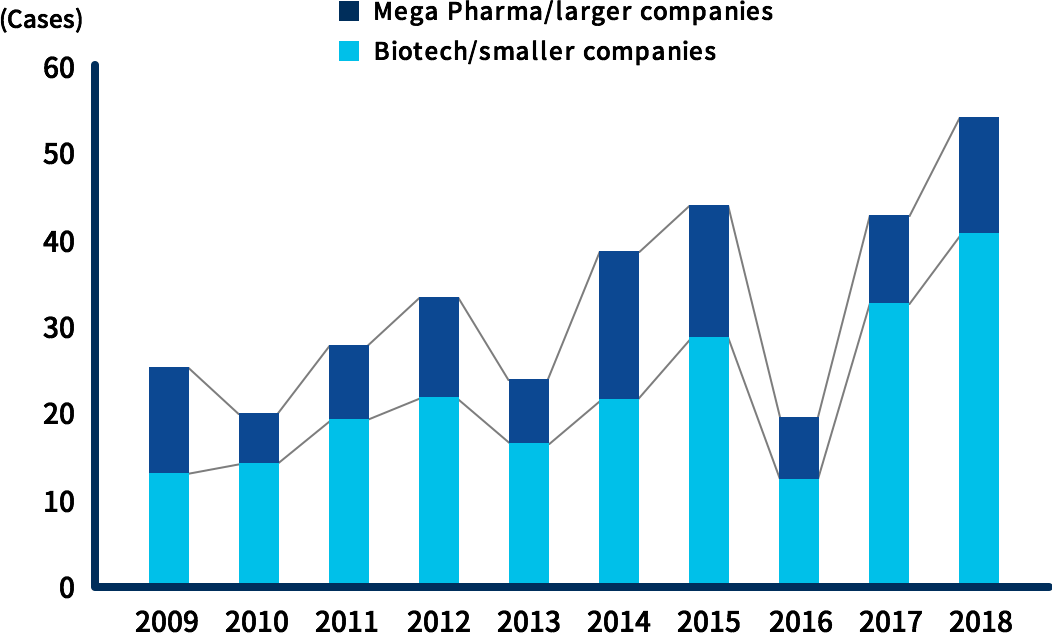
Source: HBM New Drug Approval Report
Despite the high demand for medicines in the lifestyle-related disease field, only a limited number of ventures have the know-how that can meet the expectations of major pharmaceutical companies. Therefore, there is a significant meaning for us to work on drug discovery in this field.
New pipeline of drug development ventures in
and outside Japan(by disease)
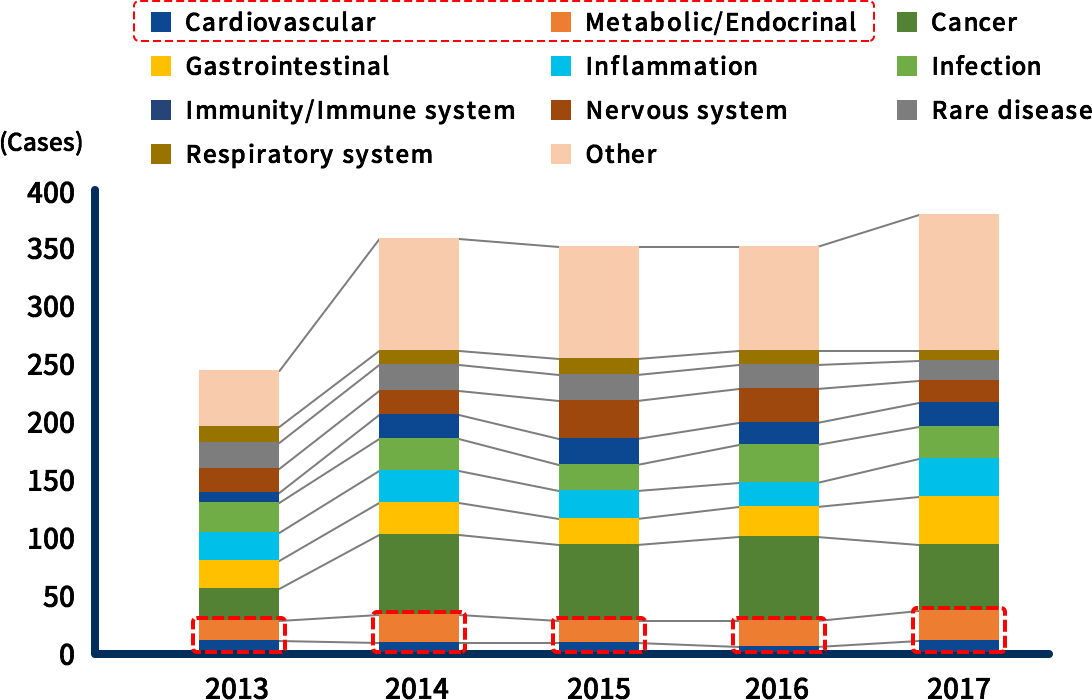
Venture companies: total market value <300 M USD
Only a few drug development ventures specialize in the field of
lifestyle-related diseases.
Strong expertise in lifestyle-related disease
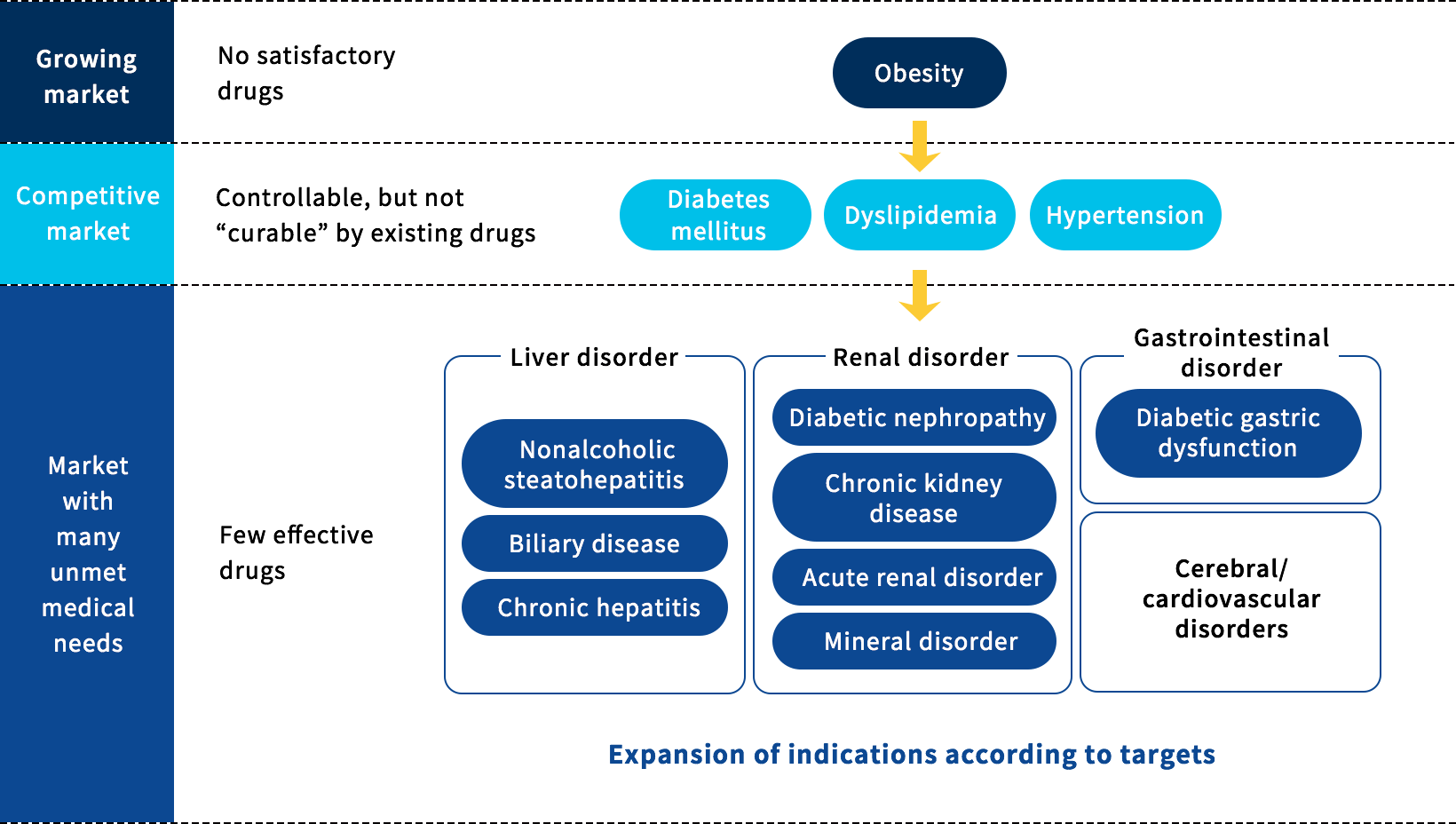
Many of our researchers have extensive experience in research and development in the field of lifestyle-related diseases at Takeda, who created a number of blockbusters, and have great expertise in drug discovery in the field. Of these, we promote R&D activities focusing on organ disorders, including chronic kidney disease, diabetic nephropathy, acute renal failure, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, in addition to obesity, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension, which require specialist knowledge.
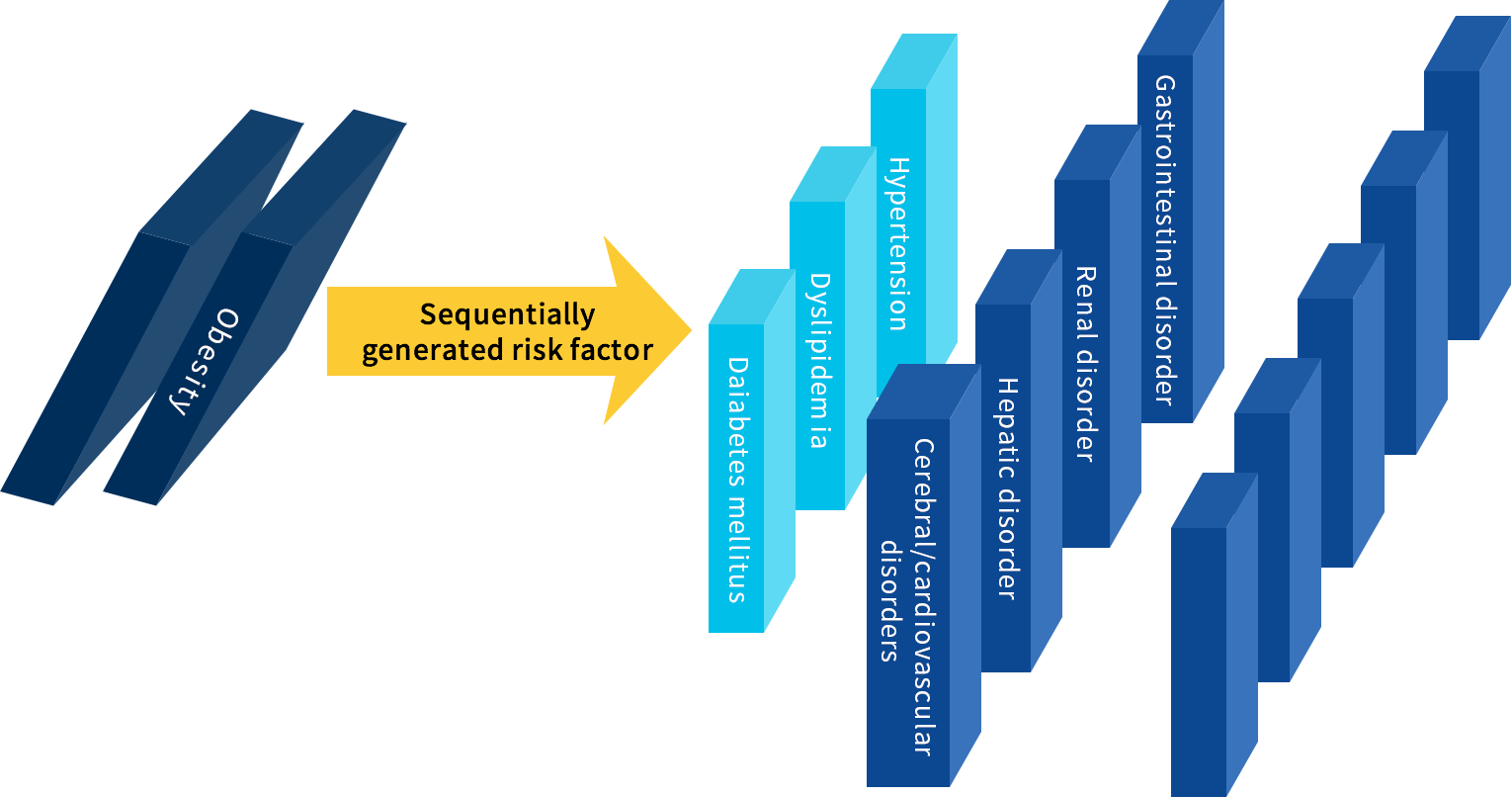
Obesity is associated with diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, leading to various complications such as diabetic nephropathy, chronic kidney disease, acute kidney injury, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, biliary diseases, chronic hepatitis, cholelithiasis, and so on.
Few existing drugs have efficacy for these complications, and we are attempting to develop drugs in such areas where adequate drug supply or effective medicines are unavailable.
If a compound is expected to be efficacious for diseases other than the above based on its characteristics, we will aim to expand the portfolio to be developed after understanding the unmet needs through market research and other methods.
Therapeutic Areas
Modality
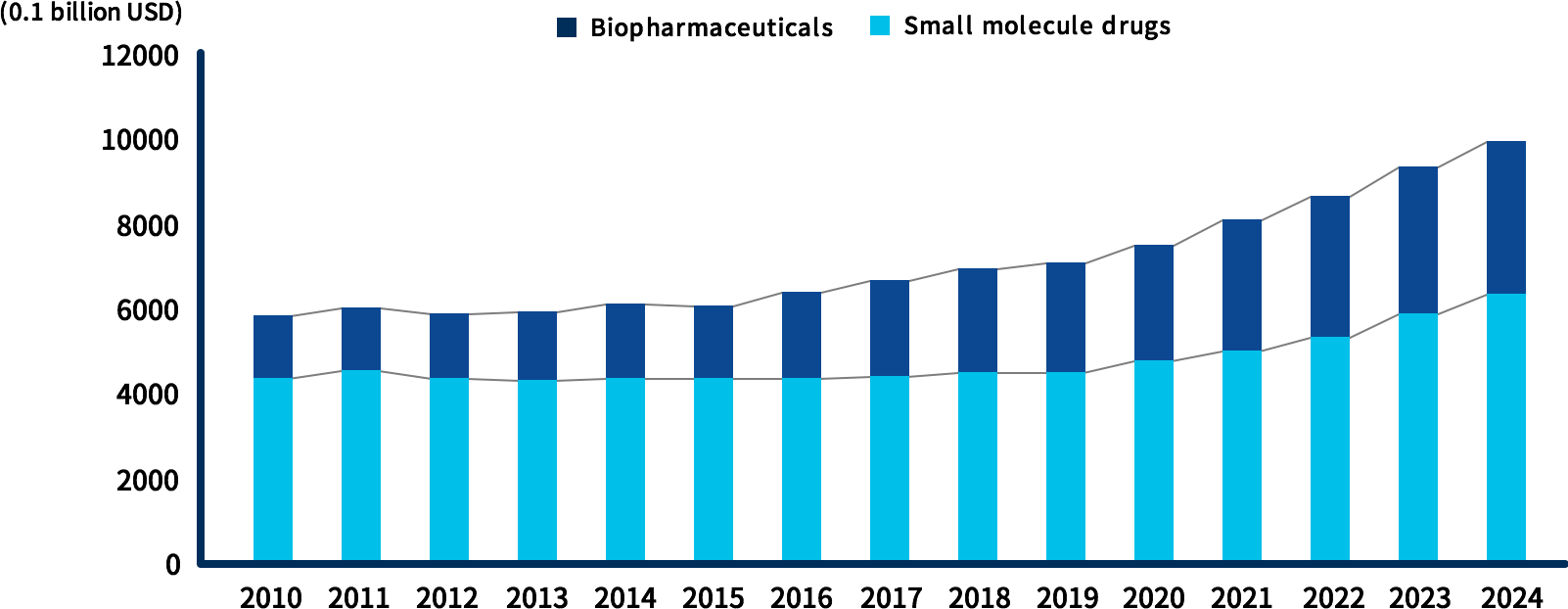
In general, drugs are classified into small, middle, and large molecules according to their molecular weight, and we are focusing on research and development of small and middle molecules.
Compared with high molecular weight biopharmaceuticals, small and middle drug molecules are often low in price and many of them are orally available, accounting for approximately two-thirds of global drug sales.
In particular, the lifestyle-related disease area has a high percentage of low molecular weight drugs under development, and we are adopting small molecules as the modality (therapeutic measures) suitable for the area.
Global drug sales
SCOHIA PHARMA has presented many research papers.
A list of papers isavailable here.

