Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) are gut hormones called incretins. They physiologically regulate metabolism and body weight via their receptors: glucagon-like polypeptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR). GLP-1R agonists are effective in improving diabetes and obesity in clinical settings. Recent advances in the combination of GIPR and GLP-1R agonists have shown superior efficacy to the GLP-1R agonist only.
SCO-094, identified by the SCOHIA researchers and collaborators, is a novel dual agonist for GLP-1R and GIPR. Preclinical studies have shown that SCO-094 is more effective in improving diabetes and obesity than the GLP-1R mono-agonist. SCO-094 is equally or more effective than that of the same class of GLP-1R/GIPR dual agonists. Moreover, SCO-094 improved liver parameters in the preclinical models with diabetes and obesity. Since a new formulation of SCO-094 demonstrated the once-weekly dosing potential in monkeys, SCOHIA is conducting studies to advance the clinical development of this regimen. The oral absorbability of SCO-094 noted in the previous studies is promising to expand the route of administration. Collectively, SCO-094 may be a new drug used to improve diabetes, obesity, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Currently, SCOHIA is conducting a phase 1 trial of the once-daily dose of SCO-094 in patients with type 2 diabetes in the UK.
SCOHIA granted worldwide exclusive rights to SCO-094 to Hangzhou Zhongmei Huadong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Indication :
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
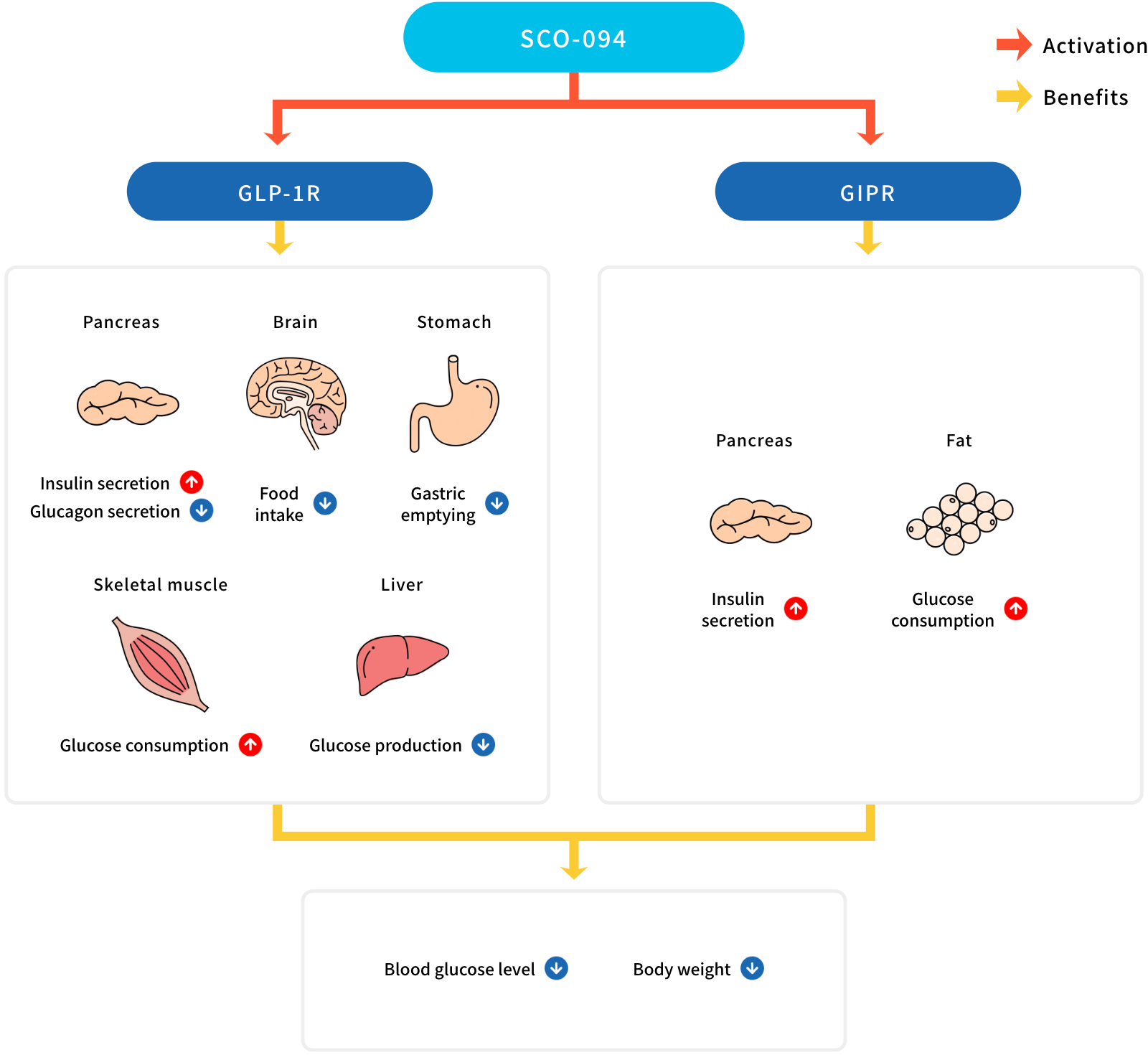
- GLP-1R : Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor
- GIPR : Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor
Clinical Trial Information
-
SCOHIA initiates a phase 1 study on a dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist (SCO-094)
Link

