The renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) is a major hormone pathway that regulates blood pressure and body fluid levels, and is involved in organ injuries. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), both of which block the downstream components of RAAS, are highly effective in controlling blood pressure and have organ protective effects, mainly on the heart and kidneys. Renin is a key upstream molecule of RAAS and its inhibition seems to result in more effective treatment than that of downstream components. However, the clinical application of a renin inhibitor is largely limited owing to the lack of efficacy.
Imarikiren (SCO-272, formerly TAK-272) is a long-acting renin inhibitor that shows excellent pharmacokinetic profiles in humans. Imarikiren has been shown to be effective in the treatment of hypertension, kidney diseases, and heart failure in preclinical studies. In addition, imarikiren sustains renin inhibition and decreases albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes.
These observations suggest that imarikiren is a novel drug candidate for the treatment of hypertension, kidney diseases, and heart failure.
Imarikiren is available as an injection, which is unusual for such a drug. Its efficacy is being investigated not only in acute treatment of hypertensive emergencies and acute heart failure, but also for blood pressure control and cardioprotection during dialysis via a vascular access.
SCOHIA is actively seeking partnerships worldwide for the development and commercialization of SCO-272 (Contact here for partnering).
Indication :
- Diabetic kidney disease
- Hypertension
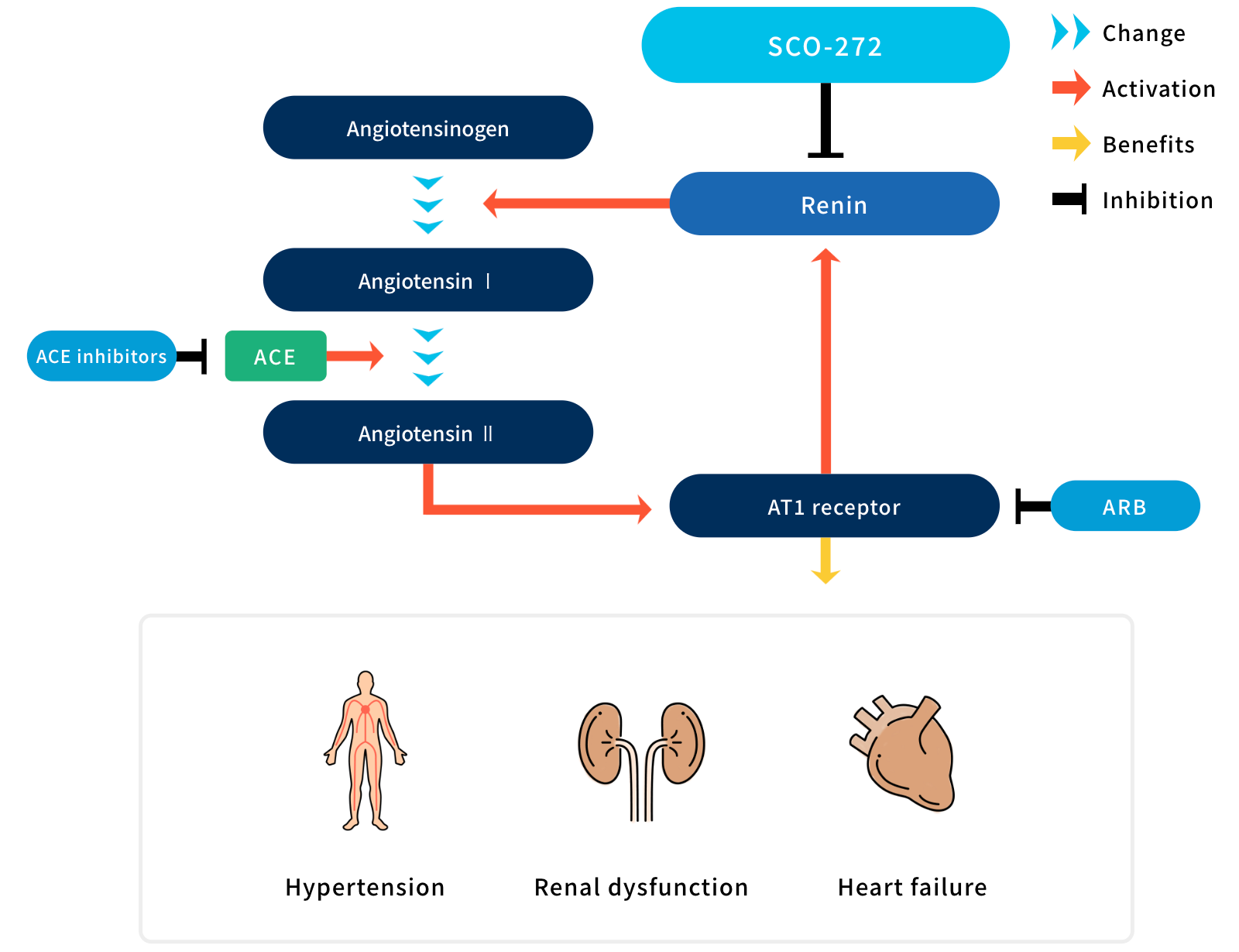
- ACE : Angiotensin-converting enzyme
- ARB : Angiotensin receptor blocker
Scientific Publication
-
Development of a novel murine heart failure model overexpressing human renin and angiotensinogen.
・FEBS Open Bio
Link -
Efficacy and Safety of Imarikiren in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Microalbuminuria: A Randomized, Controlled Trial.
・Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
Link -
Benchmarking renin suppression and blood pressure reduction of direct renin inhibitor imarikiren through quantitative systems pharmacology modeling.
・Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Link -
Pharmacokinetics and Safety After a Single Dose of Imarikiren in Subjects with Renal or Hepatic Impairment.
・Clinical Drug Investigation
Link -
Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Safety of a Single Dose of Imarikiren, a Novel Renin Inhibitor, in Healthy Male Subjects.
・Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology
Link -
A Randomized, Single-Center, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Multiple-Dose Phase 1 Study to Evaluate the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of Imarikiren in Healthy Adult Nonelderly and Elderly Male Subjects.
・The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology
Link -
The effect of elevated α1-acid glycoprotein on the pharmacokinetics of TAK-272 (SCO-272), an orally active renin inhibitor, in rats.
・Xenobiotica
Link -
Differences in nonclinical pharmacokinetics between species and prediction of human pharmacokinetics of TAK-272 (SCO-272), a novel orally active renin inhibitor.
・Biopharmaceutics&Drug Disposition
Link -
Discovery of TAK-272: A Novel, Potent, and Orally Active Renin Inhibitor.
・ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters
Link -
TAK-272 (imarikiren), a novel renin inhibitor, improves cardiac remodeling and mortality in a murine heart failure model.
・PLOS ONE
Link

