GPR40 is a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) activated by endogenous ligands of medium-to-long chain fatty acids. GPR40 is expressed in pancreatic beta-cells and enteroendocrine cells, and it physiologically regulates the secretion of insulin, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). The strategy to increase insulin secretion, and the activities of GLP-1 and GIP agonism, would be effective in improving diabetes and obesity in humans; hence, GPR40 seems to be highly attractive as a new class of drug for these patients.
GPR40 has three independent small-molecule binding sites. Fasiglifam, a GPR40 partial agonist, binds to one site of these pockets and markedly improves glycemic control by increasing insulin secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes.
SCO-267, identified by SCOHIA researchers and collaborators, is a GPR40 full agonist, which has a new chemical structure and binds to a site independent of the fasiglifam binding site. Contrary to GPR40 partial agonists, which increase insulin secretion only, a GPR40 full agonist such as SCO-267 is unique in that it increases the production of islet hormones and gut hormones.
In a Phase 1 study, a single dose of SCO-267 stimulated islet and gut hormones and remarkably improved glucose tolerance in diabetic patients.
In preclinical studies, SCO-267 increases the levels of GLP-1, GIP, and peptide YY, and thus, decreases body weight in obesity models. In addition to these hormones, SCO-267 increases insulin secretion and improves glucose control more effectively than GPR40 partial agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Furthermore, SCO-267 increases the secretion of glucagon, which has a major role in liver metabolism and function, and improves liver parameters in preclinical models with liver-dysfunctions.
Based on these observations, SCO-267 may be a new drug option for the treatment of diabetes, obesity, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Moreover, a Phase 2 study is in preparation.
SCOHIA is actively seeking partnerships worldwide for the development and commercialization of SCO-267 (Contact here for partnering).
Indication :
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
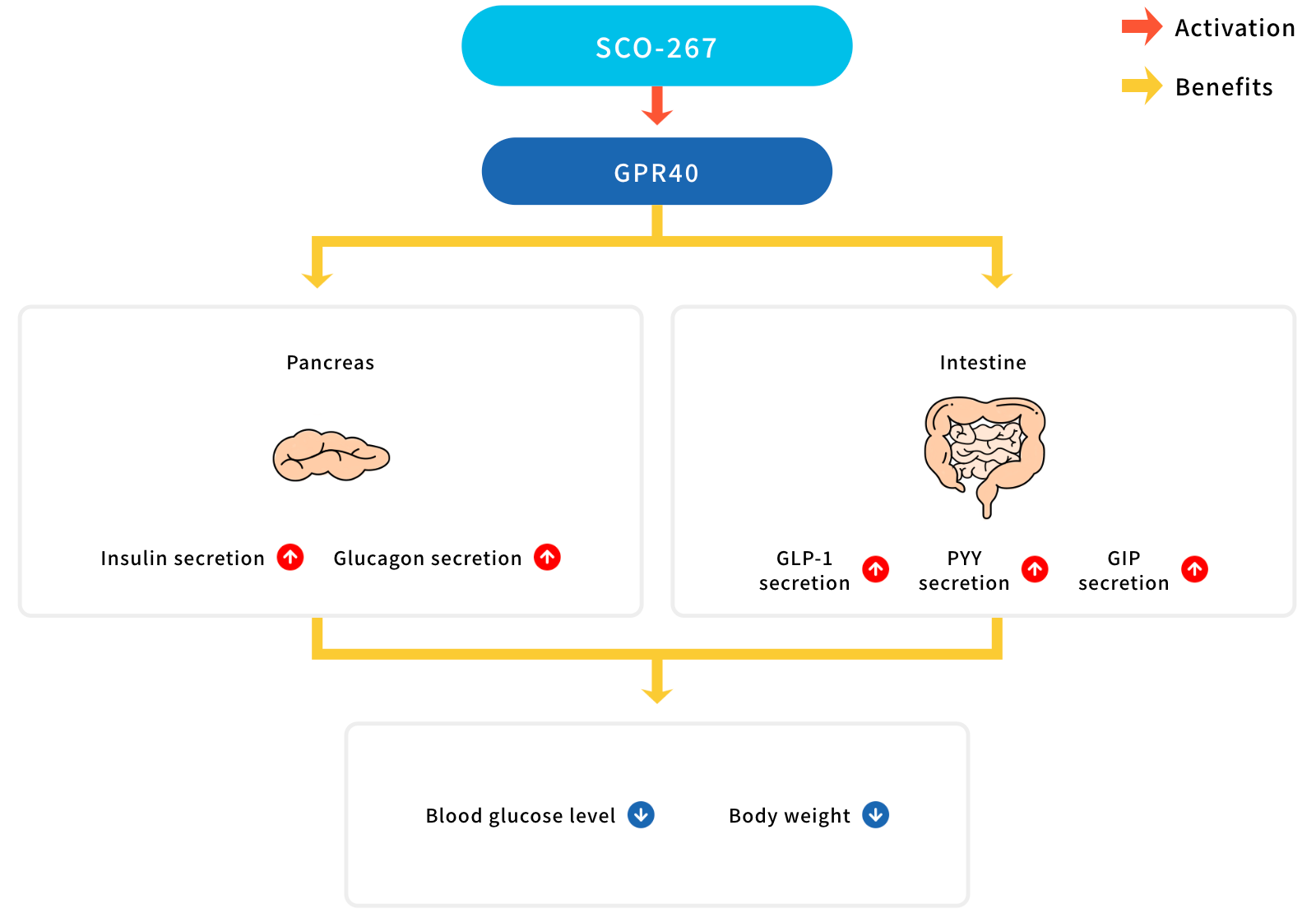
- GLP-1 : Glucagon-like peptide 1
- PYY : Peptide YY
- GIP : Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide
Clinical Trial Information
-
SCOHIA initiates a Phase 1 study of a GPR40 full agonist (SCO-267)
Link
Scientific Presentation
-
The clinical results of SCO-267 was presented at the Virtual 81st Scientific Sessions – American Diabetes Association: First report on the clinical data of a GPR40 full agonist in the phase 1 trial
Link -
Conference presentation regarding medicinal chemistry research on a GPR40 full agonist (SCO-267)
Link -
Design and Identification of a GPR40 Full Agonist (SCO-267) Possessing a 2-Carbamoylphenyl Piperidine Moiety for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
・EFMC-ISMC Virtual Event 2020
Link -
Discovery of SCO-267, a First-in-class GPR40 Full Agonist, as a Promising Candidate for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Obesity, and NASH
・EFMC-ISMC Virtual Event 2020
Link -
SCO-267, a GPR40 Full Agonist, Improves Glycemic and Body Weight Control More Than That by Fasiglifam in Rat Models of Diabetes and Obesity
・79th Scientific Sessions of American Diabetes Association held June 7-11, 2019, San Francisco, California, USA.
Link
Scientific Publication
-
Publication of a clinical phase 1 study: SCO-267, a GPR40 full agonist, is safe and well-tolerated, exhibits good potential for once-daily dosing, and improves glycemic control in humans
Link -
Publication of a preclinical study: chronic exposure to SCO-267, a GPR40, is effective in treating diabetes in preclinical models
Link -
Design and Identification of a GPR40 Full Agonist (SCO-267) Possessing a 2-Carbamoylphenyl Piperidine Moiety
・Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Link -
The GPR40 full agonist SCO-267 improves liver parameters in a mouse model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease without affecting glucose or body weight
・Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
Link -
SCO-267, a GPR40 full agonist, improves glycemic and body weight control in rat models of diabetes and obesity
・Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
Link

